Noun Phrases
A noun phrase can be only a noun: Mary loves her dog. Some experts point out that ``since each individual language only uses a subset of all possible categories, it is necessary first to investigate a noun``. (Rijikhoff, 2002 : 1). Many grammarians describe a noun as ``a word that is the name of a person, place, thing or idea: Anne, London, cat and happiness are all nouns. ``(Crawley, 2005 : 240).
The noun phrase can be only a pronoun: She loves her dog. Linguists often define a pronoun ``as a word that takes place of a noun``. (Straus, 2006 : 6). If the Head is a pronoun, the noun phrase will generally consist of Head only. This is because pronouns do not take determiners or adjectives, so there will be no pre-Head string.
The noun phrase often consists of a determiner and a noun: Her dog is very clever. Language experts indicate that ``determiner is a word that comes before a noun to show how the noun is being used: Her, most and those are all determiners``. (Steel, 2000 : 184). Determiners are: articles, demonstratives, numerals, possessives and quantifiers. For example, a quantifier which precedes a noun is: Some people do not like dogs. Many grammarians agree that: ``quantifiers are words or phrases which often modify nouns and show how many things and how much of something we are talking about``. (Alexander, 2006 : 88). Modifiers before the noun are called premodifiers (modify means to characterize, limit, restrict or otherwise focus meaning).
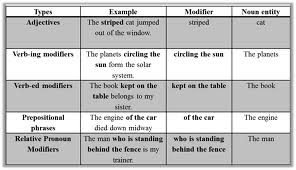
Sometimes, adverbs can precede a noun phrase: the then president. Premodifiers also include adjectives: a shy girl. Grammarians emphasize that ``adjectives are words that refer to the qualities of people, things, or ideas, or which group them into classes``. (Seely, 2009 : 5). Participles are often premodifiers as well: a subdued person, or an amazing story. Linguists point out ``that participles used as adjectives are adjectives that end with –ing or –ed``.(Fuchs and Bonner, 2007 : 177). There are two kinds of adjectives: base adjectives and strong adjectives. Base adjectives are normal adjectives that don`t have the idea of ``very``( good, hungry and bad ). When we want to describe something or someone as exceptional, we use strong adjectives (wonderful, starving and horrible). We can make adjectives more extreme by using adverbs very and absolutely. Some grammarians indicate that ``we can use very only with base adjectives and we can use absolutely only with strong adjectives’’. (Soars, 2003 : 68). However, we can use really with both base and strong adjectives. The following noun phrases illustrate these rules: a very tired man (determiner + very + base adjective + noun), an absolutely exhausted man (determiner + absolutely + strong adjective + noun), a really tired man (determiner + really + base adjective + noun) and a really exhausted man (determiner + really + strong adjective + noun).
